| RESEARCH PAPER |
|
 |
|

|
|
|
| Effect of Solution Temperature on Microstructure and Properties of TP347HFG Heat Resistant Steel |
| Hong ZHANG,Ping ZHOU,Lan SUN,Hongyuan FAN
|
| Department of Manufacturing Science and Engineering,Sichuan University, Chengdu 610065 |
|
|
|
|
Abstract TP347HFG heat resistant steel with different solution temperature were characterized by OM, SEM, hardness and tensile strength test, and its microstructure and corresponding properties were investigated as well. Results show that the grain size of TP347HFG heat resistant steel decreases as the solution temperature increases. Their crystalline sizes are evenly distributed with the solution temperature at 1 180 ℃, whereas the crystalline sizes increase and unevenly disperse at 1 210 ℃. The second phase of TP347HFG heat resistant steel, which is mainly NbC, is composed of both large particles and small particles. Small second phase precipitate at the grain boundary at 1 180 ℃ and 1 120 ℃, which can strengthen the grain boundaries. Most part of the second phase precipitate at 1 210 ℃ in the grains with simultaneous occurrence of the Ostwald ripening phenomenon, where the particle distribution of small second phase diminishes while that of larger one increases, and thus bringing the change of corresponding fundamental properties. The values of tensile strength and Rp0.2 reach their peaks with the solution temperature at 1 120 ℃ and 1 180 ℃. The elongation property of this material improves while its hardness decreases, as the increasing solution temperature.
|
|
Published: 25 January 2018
Online: 2018-01-25
|
|
|
|
|

| Element | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ni | Cr | Nb | Fe | | Content | 0.072 | 0.37 | 1.40 | 0.028 | 0.003 | 10.8 | 17.7 | 0.7 | Bal. |
|
|
Chemical composition (mass fraction,%) of TP347HFG heat resistant steel
|

| Sample | 1# | 2# | 3# | 4# | 5# | | Solution
temperature/℃ | 1 120 | 1 150 | 1 180 | 1 210 | Non heat
treatment | | Holding time/min | 20 | | | Cool type | Water cooling | |
|
|
Heat treatment of 1—5 samples
|
|
|
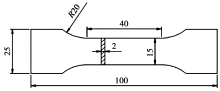
Size of the tenile sample(unit: mm)
|

|
|
The metallurgical pictures of samples with different solution treatment temperature:(a)1 120 ℃,(b)1 150 ℃, (c)1 180 ℃,(d)1 210 ℃,(e)original sample
|

Solution
temperature/℃ | 1 120 | 1 150 | 1 180 | 1 210 | Original
sample | | M | 500 | 500 | 500 | 200 | 500 | | 12.5 | 11.6 | 10.4 | 12.0 | 14.5 | | L/mm | 140 | 140 | 140 | 140 | 140 | | G | 7.7 | 7.5 | 7.1 | 4.9 | 8.1 |
|
|
Grain size of the samples
|

|
|
The SEM pictures of samples:(a)1 120 ℃,(b)1 150 ℃, (c)1 180 ℃,(d)1 210 ℃,(e)original sample
|
|
|
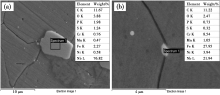
EDS analysis for the components of (a)large particles of the second phase and (b)small particles of the second phase
|

Solution
temperature/℃ | 1 120 | 1 150 | 1 180 | 1 210 | Original
sample | Tensile strength
MPa | 489 | 479 | 489 | 471 | 459 | | Rp0.2/MPa | 234 | 230 | 235 | 210 | 222 | | Elongation/% | 59.7 | 60.1 | 60.2 | 65.8 | 57.5 | | Brinell hardness | 163 | 156 | 155 | 149 | 159 |
|
|
Tensile strength, Rp0.2, elongation and hardness values of TP347HFG steel
|
| 1 | Sandhya H, Adisom A, Amomvadee V . Exergy analysis of ultra super-critical power plant[J]. Energy Procedia, 2013,37:2544. | | 2 | Gibbons T B . Superalloys in modern power generation applications[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2009,25(2):129. | | 3 | Viswanathan R, Henry J F, Tanzosh J , et al. U.S.program on materials technology for ultra-supercritical coal power plants[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2005,14(3):281. | | 4 | Iseda A, Okada H, Sembah H , et al. Long term creep properties and microstructure of SUPER304H,TP347HFG and HR3C for A-USC boilers[J]. Energy Materials, 2007,2(4):199. | | 5 | 5 彭芳芳, 彭志方, 陈方玉 . 600MW/1000MW超超临界机组新型钢国产化研讨会报告文集[R]. 扬州:中国电力期刊网, 2009: 178. | | 6 | Fu S L, Shi C C, Xi S X . Ultrasupercritical power plant development and high temperature materials applications in China[J]. Energy Materials, 2008,3(4):201. | | 7 | Yagi K, Merckling G, Kem T U , et al. Creep properties of heat resistant steels and superalloys[M]. Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 2004: 248. | | 8 | 8 刘正东, 程世长, 王起江 , 等. 中国600 ℃火电机组锅炉钢研究进展[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2011: 160. | | 9 | Peng Zhifang, Dang Yingying, Peng Fangfang . Effect of carbon and niobium on phase stability and creep rupture life at 650 ℃ for TP347HFG steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2012,48(4):450(in Chinese). | | 10 | 彭志方, 党莹樱, 彭芳芳 . C、Nb含量对TP347HFG钢在650 ℃析出相参量和持久寿命的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2012,48(4):450. | | 11 | Sounmail T . Precipitation in creep resistant austenitic stainlesssteels[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2001,17(1):1. | | 12 | 11 虞觉奇. 二元合金状态图集[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1983: 332. | | 13 | Kyu H L, Jin Y S, Joo Y H , et al. Effect of Nb and Cu on the high temperature creep properties of a high Mn-N austenitic stainless steel[J]. Materials Characterization, 2013,83(3):49. | | 14 | Onizawa T, Wakai T, Ando M , et al. Effect of V and Nb on precipitation behavior and mechanical properties of high Cr steel[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2008,238(2):408. | | 15 | Sawaragi Y, Hirano S . The development of a new 18-8 austenitic stainless steel (0.lC-18Cr-9Ni-3Cu-Nb,N)with high elevated temperatures strength for fossil power boilers[J]. Mechanical Behavior of Materials VI, 1992,4:589. | | 16 | Minami Y, Kimura H, Ihara Y . Microstructural changes in austenitic stainless steels during long-term aging[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1986,2(8):795. | | 17 | Hao Hongyuan, Cao Shirui, Hao Yao . Effect of solid solution/aging treatment on microstructure and properties of austenitic base heat resistant steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2006,31(4):65(in Chinese). | | 18 | 郝红元, 曹士锐, 郝曜 . 固溶/时效处理对奥氏体耐热钢组织与性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2006,31(4):65. | | 19 | 17 崔忠圻, 覃耀春 . 金属学与热处理[M]. 第二版.北京: 机械工业出版社, 2014. 350. | | 20 | Glandman T . The physical metallurgyofmicro alloyed steel[M]. Cambridge: The University Press, 1997: 123. | | 21 | 19 樊东黎, 徐跃明, 佟晓辉 . 热处理技术数据手册[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2006: 123. | | 22 | Zhang Wei . Inspection methods of austenitic grain size in stainless steel[J]. Material & Heat Treatment, 2010,39(22):66(in Chinese). | | 23 | 张卫 . 钢的奥氏体晶粒度检验方法[J]. 材料热处理技术, 2010,39(22):66. | | 24 | Jia Hongbin, Zhang Hongmei , et al. Austenite grain growth beha-vior of fine-grain and high-strength IF steel in heating process[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2015,44(4):56(in Chinese). | | 25 | 贾宏斌, 张红梅 , 等. 加热过程中细晶高强IF钢奥氏体晶粒长大规律研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2015,44(4):56. | | 26 | Chen Zhenyu, Hu Chuanshun, Qin Hua , et al. Effect of heating temperature on grain size of 2.25Cr-1Mo-0.25V steel[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2013,42(4):23(in Chinese). | | 27 | 陈振宇, 胡传顺, 秦华 , 等. 加热温度对2.25Cr-1Mo-0.25V钢晶粒度的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2013,42(4):23. | | 28 | Uhm S, Moom J, Lee C . Prediction model for the austenite grain size in the coarse grained heat affected zone of Fe-C-Mn steels:Considering the effect of initial grain size on isothermal growth behavior[J]. ISIJ International, 2004,44(7):1230. |
|
|
|
|

 渝公网安备50019002502923号 © Editorial Office of Materials Reports.
渝公网安备50019002502923号 © Editorial Office of Materials Reports.
 2018, Vol. 32
2018, Vol. 32 