| RESEARCH PAPER |
|
 |
|

|
|
|
| Effect of Microalloying Element Niobium on the Strength and Toughness of Low Carbon Cast Steels |
| Dingfa FU,Yu LENG,Wenli GAO
|
| College of Materials Science and Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082 |
|
|
|
|
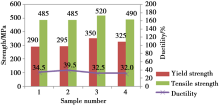
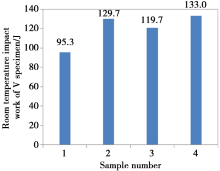
Abstract Microalloyed cast steels with different amount of niobium (Nb) were produced by medium frequency induction furnace. Optical microscopy (OM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were utilized to investigate the effect of microalloying element Nb on microstructure, strength and toughness of low carbon cast steels. The results indicated that the grain size of low carbon cast steels were refined by 20.8%—34.6% and fine NbC particles were formed by niobium addition. Meanwhile, yield strength (YS), ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and room temperature toughness of the microalloyed steels were improved significantly. Grain refining and precipitation were proved to be the main strengthening mechanisms. When the content of Nb was 0.044 wt%, the YS, UTS and impact energy of the microalloyed steel were 350 MPa, 520 MPa and 119.7 J, respectively. They were improved by 20.7%, 7.2% and 25.6% with retained ductility, respectively, as compared to Nb-free steel.
|
|
Published: 25 January 2018
Online: 2018-01-25
|
|
|
|
|

| Sample | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Al | Nb | | 1 | 0.18 | 0.49 | 0.83 | 0.021 | 0.005 | 0.07 | — | | 2 | 0.15 | 0.55 | 0.90 | 0.023 | 0.008 | 0.06 | 0.016 | | 3 | 0.18 | 0.42 | 0.94 | 0.020 | 0.006 | 0.03 | 0.044 | | 4 | 0.15 | 0.46 | 0.76 | 0.018 | 0.003 | 0.05 | 0.072 |
|
|
Chemical composition (wt%) of the investigated steels
|
|
|
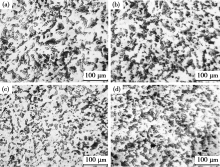
Microstructure of the investigated steels after normalizing at 900 ℃ and tempering at 550 ℃ with different Nb contents:(a)0%, (b)0.016%, (c)0.044%, (d)0.072%
|
|
|
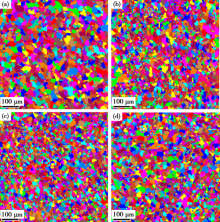
Grain morphology and size analysis of the investigated steels with different Nb contents by EBSD: (a)0%, (b)0.016%, (c)0.044%, (d)0.072%
|
|
|
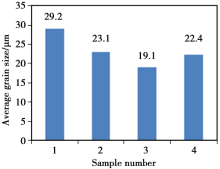
Grain size of the investigated steels with different Nb contents
|
|
|
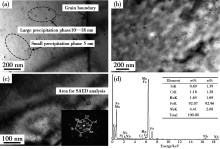
Precipitates analysis of the niobium microalloyed steels (0.044% Nb) by TEM
|
|
|
Relationship between Nb content and strength/ductility of the investigated steels
|
|
|
Relationship between Nb content and room temperature impact toughness of the investigated steels
|
| 1 | Jingwei Zhao , Zhengyi Jiang. Development of new microalloyed steel by alloying with tungsten[J].Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2015, 716- 717:48. | | 2 | Gladman T . The physical metallurgy of microalloyed steels[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002: 1. | | 3 | Liang Guoli . Analysis on tempering process of oil tank steel with low carbon and microalloy[J]. Materials Review B:Research Papers, 2015,29(9):77(in Chinese). | | 4 | 梁国俐 . 低碳微合金石油储罐钢回火工艺研究[J]. 材料导报:研究篇, 2015,29(9):77. | | 5 | Li Jie, Wang Guoliang, Xia Yunjin , et al. Effect of Nb and V Micro-alloying on the precipitation phases in Q345E for wind-electron flange[J]. Materials Review B:Research Papers, 2014,28(7):104(in Chinese). | | 6 | 李杰, 王国梁, 夏云进 , 等. 铌钒微合金化对风电法兰用Q345E钢析出相的影响[J]. 材料导报:研究篇, 2014,28(7):104. | | 7 | 5 Ma Jie, Sun Fangce, Chen Mulan, et al. Effects of microalloying elements on the structure and properties of low-alloy cast steel[J].Foundry, 1997(1):25(in Chinese). | | 8 | 马捷, 孙方策, 陈木兰 , 等. 微合金化元素对低合金铸钢组织和性能的影响[J].铸造, 1997(1):25. | | 9 | Wei Shenghui . Effects on microstructures and mechanical properties of cast steel by micro-alloying[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2009(in Chinese). | | 10 | 魏胜辉 . 微合金化对铸钢组织和力学性能的影响[D]. 石家庄:河北科技大学, 2009. | | 11 | Najafi H, Rassizadehghani J, Norouzi S . Mechanical properties of as-cast microalloyed steels produced via investment casting[J]. Materials and Design, 2011,32(2):656. | | 12 | Najafi H, Rassizadehghani J, Asgari S . As-cast mechanical properties of vanadium/niobium microalloyed steels[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008,486(s1-2):1. | | 13 | 9 Yang Zuohong, Chen Baichun. On the role of micro-alloying elements Nb, V, Ti in steel[J].Gansu Metallurgy, 2002(4):20(in Chinese). | | 14 | 杨作宏, 陈伯春 . 谈微合金元素Nb、V、Ti在钢中的作用[J].甘肃冶金, 2002(4):20. | | 15 | Wang Zubin . Development of low-alloy and microalloy steels[J]. China Metallurgy, 1999,3(4):19(in Chinese). | | 16 | 王祖滨 . 低合金钢和微合金钢的发展[J]. 中国冶金, 1999,3(4):19. | | 17 | Jingwei Zhao, Jeong Hun Lee, Yong Woo Kim , et al. Enhancing mechanical properties of a low-carbon microalloyed cast steel by controlled heat treatment[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2013,559(3):427. | | 18 | 12 Song Xiaoju, Zheng Jianhua, Luo Shixiong, et al. The behavior and effect of V, Ti, Nb, B, Re and other elements in microalloyed steels[J].CISC Technology, 2000(2):26(in Chinese). | | 19 | 宋晓菊, 郑建华, 骆世雄 , 等. V、Ti、Nb、B、Re等元素在微合金钢中的行为和作用[J].重钢技术, 2000(2):26. | | 20 | Zhao Luyu . Application of trace rare earth element in cast steel[J]. Development and Application of Materials, 2003,18(3):43(in Chinese). | | 21 | 赵路遇 . 微量稀土元素在铸钢中的应用[J]. 材料开发与应用, 2003,18(3):43. | | 22 | David Turnbull, Bernard Vonnegut . Nucleation catalysis[J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 1952,4(6):1292. | | 23 | Xie Jingpei, Wang Wenyan, Wang Aiqin , et al. Effects of Nb and N in medium manganese austenitic steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2002,14(1):38(in Chinese). | | 24 | 谢敬佩, 王文焱, 王爱琴 , 等. 铌、氮在中锰奥氏体钢中的作用[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2002,14(1):38. | | 25 | Hall E O . The deformation and ageing of mild steel: Ⅲ Discussion of results[J]. Proceedings of the Physical Society, 1951,643(9):747. | | 26 | Petch N J . The cleavage strength of polycrystals[J]. Transactions of the Iron and Steel Institute of Japan, 1953,173(1):25. | | 27 | Krauss G . Strengthening mechanisms in steels[M]. Encyclopedia of Materials Science and Technology, 2001: 8870. | | 28 | Najafi H, Rassizadehghani J, Halvaaee A . Mechanical properties of as cast microalloyed steels containing V, Nb and Ti[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2007,23(6):699. | | 29 | Rassizadehghani J, Najafi H, Emamy M , et al. Mechanical properties of V-,Nb-,and Ti-bearing as-cast microalloyed steels[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2007,23(6):779. | | 30 | Leap M J, Wingert J C . The effects of grain-refining precipitates on the development of toughness in 4340 steel[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions A, 1999,30(1):93. |
|
|
|
|

 渝公网安备50019002502923号 © Editorial Office of Materials Reports.
渝公网安备50019002502923号 © Editorial Office of Materials Reports.
 2018, Vol. 32
2018, Vol. 32 