| RESEARCH PAPER |
|
 |
|

|
|
|
| Effects of Temperature and Humidity on Porosity and Mechanical Properties of Aluminum Alloy MIG Joints |
| Jianyi QIAO1,2,Wenquan WANG1,Ye RUAN1,Chengwei GUO3
|
1 College of Materials Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130022
2 China Nuclear Power Technology Research Institute, Shenzhen 518031
3 Chengde Petroleum College, Chengde 067000 |
|
|
|
|
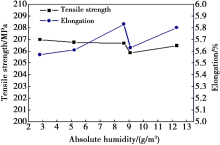
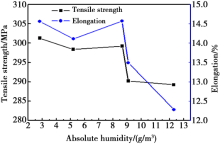
Abstract Generally speaking, porosity defect is one of the inevitable challenges encountered in the joints of aluminum alloy structures during fabrication of high speed railway vehicles. X-ray inspection was used to investigate the porosity rate of aluminum alloy 6082 joints and 5083 joints welded by metal inert gas arc welding (MIG) under different temperatures and humidity. The results demonstrated that the susceptibility of aluminum alloy 6082 welded joints to porosity was higher than that of 5083 welded joints. The porosity rate in aluminum alloy joints was almost determined by the absolute humidity in the welding environment. During the tensile strength test, the fractures of the welded aluminum alloy 6082 joints were mainly located in the heat affected zone (HAZ). With the increase of the absolute humidity, the tensile strength and elongation of the 6082 joints remained almost stable. However, the front and back bending angles of the joints were reduced by 74.4% and 64.4%, respectively. The fractures of the welded aluminum alloy 5083 joints were mainly located in the fusion zone. With the increase of the absolute humidity, the tensile strength and elongation of the 5083 joints decreased by 4.0% and 15.7%, respectively. Whereas, the bending capacity of the 5083 joints was hardly affected by the humidity variation in the welding environment.
|
|
Published: 25 January 2018
Online: 2018-01-25
|
|
|
|
|

| Material | Tensile strength
MPa | Elongation
% | Thermal conductivity
(20 ℃)/(W/(m·K)) | | 6082 | 349.9 | 9.9 | 174 | | 5083 | 310.1 | 22.8 | 117 |
|
|
Mechanical and physical properties of aluminum alloys 6082 and 5083
|
|
|
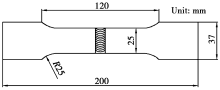
The shape and size of tensile specimen
|
|
|
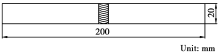
The shape and size of bending specimen
|

| Temperature/℃ | Humidity/% | X-ray inspections and image analysis | Porosity/% | Aluminum
alloy 6082 | 10 | 30 | | 1.43 | | 20 | 30 | | 1.66 | | 20 | 50 | | 1.86 | | 20 | 70 | | 2.19 | | 30 | 30 | | 1.93 |
|
|
The porosity rate of aluminum alloys 6082 and 5083 weld beads
|

| Temperature/℃ | Humidity/% | X-ray inspections and image analysis | Porosity/% | Aluminum
alloy 5083 | 10 | 30 | | 0.16 | | 20 | 30 | | 0.19 | | 20 | 50 | | 0.34 | | 20 | 70 | | 0.56 | | 30 | 30 | | 0.41 |
|
|
Xu
|

| Temperature/℃ | 10 | | 20 | | 30 | | Relative humidity/% | 30 | 30 | 50 | 70 | 30 | Saturated humidity
g/m3 | 9.35 | | 17.30 | | 30.30 | Absolute humidity
g/m3 | 2.81 | 5.19 | 8.65 | 12.32 | 9.09 |
|
|
Absolute humidity under different temperature and relative humidity
|
|
|
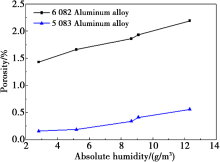
Effect of absolute humidity on porosity
|
|
|
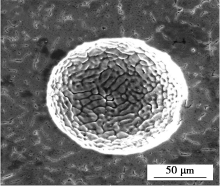
Morphology of hydrogen pore in weld bead
|
|
|
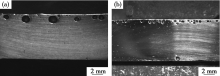
Morphology of subsurface pores in longitudinal section of (a) 6082 weld bead and (b) 5083 weld bead
|
|
|
Effects of absolute humidity on tensile strength and elongation of 6082 joints
|
|
|
Effects of absolute humidity on tensile strength and elongation of 5083 joints
|

|
|
Pores distribution on the fracture surface of joint: (a)tensile fracture of 5083 joint;(b)bending fracture 6082 joint
|

Absolute
humidity/(g/m3) | Pressure head
diameter/mm | 6082 welded joint | 5083 welded joint | Front bending
angle/(°) | Back bending
angle/(°) | Front bending
angle/(°) | Back bending
angle/(°) | | 2.81 | 30 | 101 | 109 | 180 | 180 | | 5.19 | 30 | 180 | 180 | 180 | 180 | | 8.65 | 30 | 54 | 74 | 180 | 180 | | 9.09 | 30 | 74 | 66 | 180 | 180 | | 12.32 | 30 | 46 | 64 | 180 | 180 |
|
|
Effect of absolute humidity on bending properties of 6082 and 5083 joints
|
| 1 | 1 王元良, 陈辉 . 高速列车铝合金车体的焊接技术[M]. 成都: 西南交通大学出版社, 2012: 12. | | 2 | Lee W B, Yeon Y M, Jung S B . Evaluation of the microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded 6005 aluminum alloy[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2003,19(11):1513. | | 3 | Gou G, Zhang M, Chen H , et al. Effect of humidity on porosity, microstructure, and fatigue strength of A7N01S-T5 aluminum alloy welded joints in high-speed trains[J]. Materials & Design, 2015,85:309. | | 4 | Haboudou A, Peyre P, Vannes A B , et al. Reduction of porosity content generated during Nd∶YAG laser welding of A356 and AA5083 aluminium alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2003,363(1):40. | | 5 | Pastor M, Zhao H, Martukanitz R P , et al. Porosity, underfill and magnesium loss during continuous wave Nd∶YAG laser welding of thin plates of aluminum alloys 5182 and 5754[J]. Welding Journal, 1999,78(6):207s. | | 6 | Ashton R F, Wesley R P, Dixon C R . The effect of porosity on 5086-H116 aluminum alloy welds[J]. Welding Research, 1975,54(3):95s. | | 7 | Wang J, Wang G Z, Wang C M . Mechanisms of the porosity formation during the fiber laser lap welding of aluminium alloy[J]. Metalurgija, 2015,54(4):683. | | 8 | Davis J R . ASM specialty handbook: Aluminum and aluminum Alloys[M]. 3rd ed.OH:ASM International, 1993. | | 9 | Liu H I, Li X P, Rui Y N . Monitor on-line and fault diagnosis to high speed centrifugal hydrogen compressors based on the theories of EMD and correlation dimension[J]. Applied Mechanics & Materials, 2010,33:523. | | 10 | J. D.法斯特.刁伟涛,梁新邦译.金属中的气体[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1983: 134. | | 11 | 11 陈伯蠡. 焊接工程缺欠分析与对策[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1997: 207. | | 12 | И. К帕豪德涅.焊缝中的气体[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1977: 197. | | 13 | 13 张文钺. 焊接冶金学[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 1999. | | 14 | 14 周敏惠, 於美甫 . 焊接缺陷与对策[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术文献出版社, 1989. | | 15 | 15 张汉谦. 钢熔焊接头金属学[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2001. | | 16 | Marioara C D, Andersen S J, Jansen J , et al. The influence of temperature and storage time at RT on nucleation of the β″ phase in a 6082 Al-Mg-Si alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2003,51(3):789. | | 17 | Qiao Jianyi, Shao Youfa, Ruan Ye , et al. Microstructure and pro-perties of MIG welding joint of aluminum alloy 6082 and 5083[J]. Materials Review B: Research Papers, 2016,30(12):94(in Chinese). | | 18 | 乔建毅, 邵有发, 阮野 , 等. 铝合金6082和5083 MIG焊接头的微观组织和性能[J]. 材料导报:研究篇, 2016,30(12):94. |
|
|
|
|

 渝公网安备50019002502923号 © Editorial Office of Materials Reports.
渝公网安备50019002502923号 © Editorial Office of Materials Reports.
 2018, Vol. 32
2018, Vol. 32 