| REVIEW PAPER |
|
 |
|

|
|
|
| A Review of the Preparation Techniques for Porous Amorphous Alloys and Their Composites |
| Zhengrong FU,Xiuchang WANG,Qinglin JIN,Jun TAN
|
| School of Materials Science and Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650093 |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Porous amorphous alloy is an emerging structural and/or functional material combined the both advantages of metallic foams and glassy alloys, which has reflected the light-weight, high-strength, and large-toughness are unified. Recently,porous amorphous alloys and their composites have exert tremendous fascination on researchers at home and abroad because of their excellent physical and chemical properties,such as high strength, low elastic modulus,high elastic strains,high corrosion resistance, and so on. In this paper,the research progress of porous amorphous alloys and their composites have been summarized.
|
|
Published: 10 February 2018
Online: 2018-02-10
|
|
|
|
|

| Ingredient | Porosity/% | Aperture/μm | E/GPa | σ/MPa | ε/% | Year | Reference | | Pd43Ni10Cu27P20 | 84 | 100—1 000 | | | | 2003 | [11] | | Pd42.5Cu30Ni7.5P20 | 65 | 125—250 | 5.2 | 75 | 1.8 | 2003 | [12] | | Zr57Nb5Cu15.4Ni12.6Al10 | 60 | 25—50 | | | | 2004 | [26] | | Pd35Pt15Cu30P20 | 45 | 200 | 27 | 400 | >30 | 2005 | [15] | | Ti36Y20Al24Co20 | | 0.015—0.155 | | | | 2006 | [45] | | Ni59Zr20Ti16Si2Sn3 | 40 | 10—50 | | 350 | 3.25 | 2006 | [49] | | Cu47Ti33Zr11Ni8Si1 | 25 | 0.02—0.5 | | | | 2006 | [52] | | Zr55Cu30Al10Ni5 | 33.5 | | 16 | 93 | >3 | 2006 | [30] | | Zr47Ti13Cu11Ni10Be16Nb3 | 80 | 150-200 | | 820 | 1.3 | 2007 | [31] | | Fe48Cr15Mo14Y2C15B6 | 65 | | | | | 2007 | [53] | | Zr57Nb5Al10Ni12.6Cu15.4 | 60.4 | 50 | 17 | 180 | >16 | 2007 | [33] | | Mg60Cu21Ag7Gd12 | 57.5 | 2 000 | 8.5 | 109 | 90 | 2007 | [56] | | Zr48Cu36Al8Ag8 | 13 | | 71 | 1 390 | 0.02 | 2008 | [34] | | Zr58.5Nb2.8Cu15.6Ni12.8Al10.3 | 60 | 45—106 | | 62 | 70 | 2009 | [25] | | Hf44.5Cu27Ni13.5Ti5Al10 | 62 | 45—106 | | | 80 | 2012 | [57] | | Zr41.25Ti13.75Cu12.5Ni10Be22.5 | 65 | | | 30 | 0.29 | 2012 | [37] | | Pd40Cu30Ni10P20 | | 20—550 | | | | 2012 | [22] | | Zr56.3Nb5.1Cu15.6Ni12.9Al10 | 70 | 45-106 | | | | 2013 | [39] | | Zr35Ti30Be26.75Cu8.25 | | 20—550 | | | | 2013 | [44] | | Ti45Zr10Cu31Pd10Sn4 | 60 | 125—250 | | | | 2014 | [46] | | Ti42Zr40Ta3Si15 | 14 | | 337 | 52 | 0.67 | 2016 | [47] | | Fe82Nb6B12 | 23—38 | 0.12 | | | | 2017 | [55] |
|
|
The first reported year,pore structure parameters and mechanical properties of various amorphous alloy foams and their composites
|
|
|
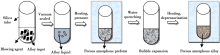
The process of porous amorphous alloys prepared by melting with foaming agent
|
|
|
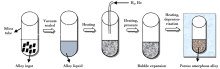
The process of porous amorphous alloys prepared by gas injection
|
|
|
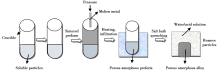
The process of porous amorphous alloys prepared by infiltration casting method with easily soluble particle
|
|
|
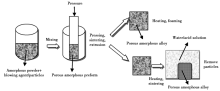
The process of porous amorphous alloys prepared by powder sintering
|
|
|
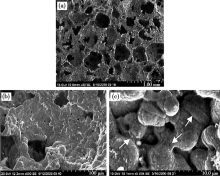
SEM images of porous Zr55Cu30Al10Ni5 bulk metallic glasses with porosity of 70%[32]:(a) the as-produced foam synthesized by hot pressing;(b) the cellular structure of the as-produced foam;(c) magnified view of the inner wall of the foam (the arrows representing bonding region between particles)
|
|
|
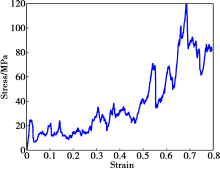
The compressive stress-strain curve of an 86% porosity foam deformed toward full densification[17]
|
|
|
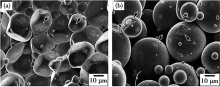
SEM micrographs of the transverse cross section of the sintered porous Zr55Cu30Al10Ni5 bulk glassy alloys with porosities of (a) 4.7% and (b) 33.5%[30]
|
|
|
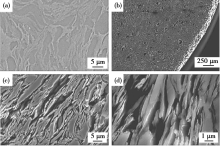
SEM images of porous Cu47Ti33Zr11Ni8Si1 metallic glass with porosity of 25%[52]:(a) transverse polished cross section of precursor before dissolution of the Cu;(b) macrostructure of porous metallic glass;(c) transverse cross-sectional microstructure metallic glass; (d) enlarged image of (c)
|
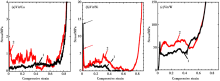
|
|
Uniaxial compressive stress-strain curves of Zr58.5Nb2.8Cu15.6Ni12.8Al10.3 foam[25]:(a)porosities of 57% and 64% from Vit/Cu;(b)porosities of 57% and 59% from Vit/Ni;(c)porosities of 59.5% and 63% from Vit/W
|
|
|
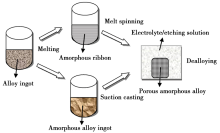
The process of porous amorphous alloys prepared by dealloying
|
|
|
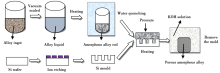
The process of porous amorphous alloys prepared by processing in supercooled liquid region
|
| 1 | Kader M A, Islam M A, Hazell P J , et al. Modelling and characterization of cell collapse in aluminium foams during dynamic loading[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016,96:78. | | 2 | Wang H, Xiao S G, Zhang T . Fabrication of nanoporous silver by de-alloying Cu-Zr-Ag amorphous alloys[J]. International Journal of Minerals,Metallurgy,and Materials, 2016,23(7):835. | | 3 | Daudt Nd F, Bram M , Barbosa A P C,et al.Manufacturing of highly porous titanium by metal injection molding in combination with plasma treatment[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2017,239:202. | | 4 | Kader M A, Islam M A, Saadatfar M , et al. Macro and micro collapse mechanisms of closed-cell aluminium foams during quasi-static compression[J]. Materials & Design, 2017,118:11. | | 5 | Pia G, Delogu F . Hardening of nanoporous Au foams induced by surface chemistry[J]. Materials Letters, 2017,196:332. | | 6 | Amsterdam E , De Hosson J Th M,Onck P R.On the plastic collapse stress of opencell aluminum foam[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2008,59(6):653. | | 7 | Ashby M F, Greer A L . Metallic glasses as structural materials[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006,54(3):321. | | 8 | Schuh C A, Hufnagel T C, Upadrasta Ramamurty . Mechanical beha-vior of amorphous alloys[J]. Acta Materialia, 2007,55:4067. | | 9 | Zhou M, Hagos K, Huang H , et al. Improved mechanical properties and pitting corrosion resistance of Zr65Cu17.5Fe10Al7.5 bulk metallic glass by isothermal annealing[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2016,452:50. | | 10 | Trady S, Mazroui M, Hasnaoui A , et al. Molecular dynamics study of atomiclevel structure in monatomic metallic glass[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2016,443:136. | | 11 | Schroers J, Veazey C, Johnson W L . Amorphous metallic foam[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2003,82(3):370. | | 12 | Wada T, Inoue A . Fabrication,thermal stability and mechanical pro-perties of porous bulk metallic glassy Pd-Ni-Cu-P alloy[J]. Materials Transactions, 2003,44(10):2228. | | 13 | Wada T, Inoue A . Formation of porous Pd-based bulk glassy alloys by a high hydrogen pressure melting-water quenching method and their mechanical properties[J]. Materials Transactions, 2004,45(8):2761. | | 14 | Schroers J, Veazey C, Demetriou M D , et al. Synjournal method for amorphous metallic foam[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2004,96(12):7723. | | 15 | Wada T, Takenaka K, Nishiyama N , et al. Formation and mechanical properties of porous Pd-Pt-Cu-P bulk glassy alloys[J]. Materials Transactions, 2005,46(12):2777. | | 16 | Wada T, Kinaka M, Inoue A . Effect of volume fraction and geometry of pores on mechanical properties of porous bulk glassy Pd42.5Cu30-Ni7.5P20 alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2006,21(4):1041. | | 17 | Demetriou M D, Schramm J P, Veazey C , et al. High porosity metallic glass foam:A powder metallurgy route[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2007,91(16):161903. | | 18 | Demetriou M D, Veazey C, Schroers J , et al.Expansion evolution during foaming of amorphous metals[J].Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2007, 449- 451:863. | | 19 | Demetriou M D, Veazey C, Schroers J , et al.Thermo-plastic expansion of amorphous metallic foam[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 434- 435:92. | | 20 | Wada T, Inoue A . Production of bulk glassy alloy foams by high pressure hydrogen[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2007,447(1-2):254. | | 21 | Demetriou M D, Veazey C, Harmon J S , et al. Stochastic metallic-glass cellular structures exhibiting benchmark strength[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008,101(14):145702. | | 22 | Xia T, Li N, Wu Y , et al. Patterned superhydrophobic surface based on Pd-based metallic glass[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2012,101(8):081601. | | 23 | Wang S, Zhang C, Li H , et al. Enhanced electro-catalytic perfor-mance of Pd-based amorphous nanoporous structure synthesized by dealloying Pd32Ni48P20 metallic glass[J]. Intermetallics, 2017,87:6. | | 24 | Cox M E, Mathaudhu S N, Hartwig K T , et al. Amorphous Zr-based foams with aligned,elongated pores[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2009,41(7):1706. | | 25 | Marchi C S, Brothers A , Dunand D C.Melt infiltration processing of foams using glass-forming alloys[J].Materials Research Society, 2003, 754:CC1. 8. 1. | | 26 | Brothers A H, Dunand D C . Syntactic bulk metallic glass foam[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2004,84(7):1108. | | 27 | Brothers A H, Dunand D C . Ductile bulk metallic glass foams[J]. Advanced Materials, 2005,17(4):484. | | 28 | Brothers A H, Dunand D C . Plasticity and damage in cellular amorphous metals[J]. Acta Materialia, 2005,53(16):4427. | | 29 | Brothers A H, Scheunemann R , DeFouw J D,et al.Processing and structure of open-celled amorphous metal foams[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2005,52(4):335. | | 30 | Xie G Q, Zhang W , Louzguine-Luzgin D V,et al.Fabrication of porous Zr-Cu-Al-Ni bulk metallic glass by spark plasma sintering process[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006,55(8):687. | | 31 | Chen X H, Zhang Y, Zhang X C , et al. A porous bulk metallic glass with unidire-ctional opening pores[J]. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 2007,10(12):E21. | | 32 | Qiu K Q, Yu B, Ren Y L . Porous bulk metallic glass fabricated by powder hot pressing[J]. University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2007,14(S1):59. | | 33 | Wada T, Qin F X, Wang X M , et al. Preparation of open-cell porous Zr-based bulk glassy alloy[J]. Materials Transactions, 2007,48(9):2381. | | 34 | Wada T, Wang X M, Kimura H , et al. Preparation of a Zr-based bulk glassy alloy foam[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2008,59(10):1071. | | 35 | Wada T, Wang X M, Kimura H , et al. Supercooled liquid foaming of a Zr-Al-Cu-Ag bulk metallic glass containing pressurized helium pores[J]. Materials Letters, 2009,63(11):858. | | 36 | Qiu K Q, Zhao Y H, Ren Y L , et al. Fabrication and mechanical properties of porous Zr-based bulk metallic glass[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009,19(5):900(in Chinese). | | 36 | 邱克强, 赵宇航, 任英磊 , 等. Zr基非晶合金多孔材料的制备与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009,19(5):900. | | 37 | Wei X, Chen J H, Dai L H . Energy absorption mechanism of open-cell Zr-based bulk metallic glass foam[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2012,66:721. | | 38 | Lin H, Wang H Y, Lu C , et al. A metallic glass syntactic foam with enhanced energy absorption performance[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2016,119:47. | | 39 | Cox M E, Dunand D C . Anisotropic mechanical properties of amorphous Zr-based foams with aligned,elongated pores[J]. Acta Mate-rialia, 2013,61(16):5937. | | 40 | Li J B, Lin H C , Jang J S C,et al.Novel open-cell bulk metallic glass foams with promising characteristics[J]. Materials Letters, 2013,105:140. | | 41 | Li N, Xia T, Heng L , et al. Superhydro-phobic Zr-based metallic glass surface with high adhesive force[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2013,102(25):251603. | | 42 | Li N, Chen Y, Jiang M Q , et al. A thermoplastic forming map of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass[J]. Acta Materialia, 2013,61(6):1921. | | 43 | Sarac B, Schroers J . Designing tensile ductility in metallic glasses[J]. Nature Communications, 2013,4:2158. | | 44 | Li X, Xu H, Jin Y , et al. Fabrication of highly ordered nanotube layer on Zr-based bulk metallic glass for biomedical uses[J]. Materials Letters, 2017,200:63. | | 45 | Jayaraj J, Park B J, Kim D H , et al. Nanometer-sized porous Ti-based metallic glass[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006,55(11):1063. | | 46 | Xie G, Qin F, Zhu S , et al. Corrosion behaviour of porous Ni-free Ti-based bulk metallic glass produced by spark plasma sintering in Hanks’ solution[J]. Intermetallics, 2014,44:55. | | 47 | Nicoara M, Raduta A, Parthiban R , et al. Low Young’s modulus Ti-based porous bulk glassy alloy without cytotoxic elements[J]. Acta Biomater, 2016,36:323. | | 48 | Sopha H, Pohl D, Damm C , et al. Self-organized double-wall oxide nanotube layers on glass-forming Ti-Zr-Si(-Nb) alloys[J]. Materials Science Engineering:C, 2017,70:258. | | 49 | Lee M H, Sordelet D J . Synjournal of bulk metallic glass foam by powder extrusion with a fugitive second phase[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2006,89(2):021921. | | 50 | Yuan L S, Zheng Y X, Jia M L , et al. Nanoporous nickel-copper-phosphorus amorphous alloy film for methanol electro-oxidation in alkaline medium[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015,154:54. | | 51 | Wang X L, Zheng Y X, Jia M L , et al. Formation of nanoporous NiCuP amorphous alloy electrode by potentio-static etching and its application for hydrazine oxidation[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016,41(20):8449. | | 52 | Lee M H, Sordelet D J . Nanoporous metallic glass with high surface area[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006,55(10):947. | | 53 | Demetriou M D, Gang D, Veazey C , et al. Amorphous Fe-based metal foam[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007,57(1):9. | | 54 | Zhang S D, Zhang W L, Wang S G , et al. Characterisation of three-dimensional porosity in an Fe-based amorphous coating and its correlation with corrosion behaviour[J]. Corrosion Science, 2015,93:211. | | 55 | Jin Y, Li R, Xu H , et al. A new strategy to fabricate nanoporous iron-based meta-llic glasses:Selective phase tailoring of amorphous-nanocrystalline composite alloys through electrochemical dissolution[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2017,133:14. | | 56 | Brothers A H, Dunand D C, Zheng Q , et al. Amorphous Mg-based metal foams with ductile hollow spheres[J]. Journal of Applied Phy-sics, 2007,102(2):023508. | | 57 | Cox M E, Kecskes L J, Mathaudhu S N , et al. Amorphous Hf-based foams with aligned,elongated pores[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2012,533:124. | | 58 | Chen X, Ouyang H W, Huang S C , et al. Production of Al-based amorphous alloy powders by close-coupled gas atomization[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2008,30(1):35(in Chinese). | | 58 | 陈欣, 欧阳鸿武, 黄誓成 , 等. 紧耦合气雾化制备Al基非晶合金粉末[J]. 北京科技大学学报, 2008,30(1):35. | | 59 | Lu C W, Lu Z C, Sun K , et al. The preparation of Fe74Al4Sn2P10-C2B4Si4 amorphous alloy powders by water atomization and magnetic powder cores performance research[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2006,55(5):2553(in Chinese). | | 59 | 陆曹卫, 卢志超, 孙克 , 等. 水雾化制备Fe74Al4Sn2P10C2B4Si4非晶合金粉末及其磁粉芯性能研究[J]. 物理学报, 2006,55(5):2553. | | 60 | White R L . The preparation of Nb3Sn superconducting alloying by mechanical alloying[D]. California:Stanford University, 1997. | | 61 | Koch C C, Cavin O B , McKamey C G,et al.Preparation of amorphous Ni60Nb40 by mechanical alloying[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 1983,43:1017. | | 62 | Schwarz R B, Petrich R R, Saw C K . The synjournal of amorphous Ni-Ti alloy powders by mechanical alloying[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 1985,76(2-3):281. | | 63 | Tang S H, Wang H X, Wang Z J , et al. Magnetic properties of amorphous Fe78Si9B13 powder prepared by ribbon crush and powder core using same[J]. Metallic Functional Materials, 2010,17(3):9(in Chinese). | | 63 | 唐书环, 王红霞, 王正杰 , 等. 带材破碎制备Fe78Si9B13非晶合金粉末及其磁粉芯性能[J]. 金属功能材料, 2010,17(3):9. | | 64 | 黄培云 . 粉末冶金原理[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1988: 99. | | 65 | Schafcr L , Fryda M.Chemical vapour deposition of polycrystalline diaond film on high-speed steel[J].Surface Coatings Technology, 1999, 116- 119:447. | | 66 | Silva F J G . Microwave plasma chemical vapour deposition diamond nucleation on ferrous subst rates with Ti and Cr interlayers[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2002,11:1617. | | 67 | Fan Q H . Diamond coating on steel with a titanium interlayer[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 1998,7:603. | | 68 | Chen Y . Chemical preparation and characterization of metal-metalloid ultrafine amorphous alloy panicles[J].Catalysis Today,l998, 44(4):15. | | 69 | Qiao M H, Xie S H, Dai W L . Ultrafine Ni-Co-W-B amorphous alloys and their activities in hydrogenation to cyclohexane[J]. Catalysis Letters, 2001,71(3):187. | | 70 | Van Wonterghem J, Morup S, Charles S W . Fonnation of ultrafine amorphous alloy particles by reduction in aqueous solution[J]. Nature, 1986,322(6080):622. | | 71 | 张立德 . 纳米材料[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2000. | | 72 | Saida J, Inoue A, Masumoto T . Effect of reaction condition on composition and properties of ultrafine amorphous powders in(Fe,Co,Ni)-B systems prepared by chemical reduction[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1991,22A(9):2125. | | 73 | Shen J Y, Li Z Y, Yan Q J . Reactions of bivalent metal ions with borohydride in aqueous solution for the preparation of ultrafine amorphous alloy particles[J]. Journals of Physics and Chemistry, 1993,97(32):8504. | | 74 | Linderoth S, Mrap S . Chemically prepared amorphous Fe-B particles:Influence of PH on the composition[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1990,67(9):4472. | | 75 | Inoue A, Saida J, Samuoto T . Formation of ultrafine amorphous powders in Fe-M-B(M=transition metal)systems by chemical reduction method and their thermal and magnetic properties[J]. Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 1988,19A(9):2315. | | 76 | Hu Z, Chen Y, Hsia Y F . U1trafine amorphous Fe-Ni-B and Fe-P-B Particles[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B, 1993,76(4):121. | | 77 | Zhang J G . Properties and structure of ultrafine amorphous Fe-Ni-B powder obtained by borohydride reduction[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and performance, 1995,4(4):453. | | 78 | DragieVa I, GaVrilo V G, BuchkoV D . The synjournal of boride powders and some of their magnetic properties[J]. Journal of the Less·Common Metals, 1979,67(2):375. | | 79 | Lee S P, Chen Y W . Nitrobenzene hy-drogenation on Ni-P,Ni-B and Ni-P-B ultrafine[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A:Chemical, 2000,152(2):213. | | 80 | Kim T S, Lee J K, Kim H J , et al. Consolidtion of Cu54Ni6Zr22Ti18 bulk amorphous alloy powders[J]. Materials Science Engineering:A, 2005,402:228. | | 81 | Segal V M . Equal channel angular extrusion from macromechanics to structure formation[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 1999,271:322. |
|
|
|
|

 渝公网安备50019002502923号 © Editorial Office of Materials Reports.
渝公网安备50019002502923号 © Editorial Office of Materials Reports.
 2018, Vol. 32
2018, Vol. 32 