| REVIEW PAPER |
|
 |
|

|
|
|
| Recent Advances in the Research of High-strength and High-conductivity CuCrZr Alloy |
| Haoqi HU1,2,Cheng XU2,Lijing YANG2,Henghua ZHANG1,Zhenlun SONG2
|
1 School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200072
2 Key Laboratory of Marine Materials and Related Technologies, Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Marine Materials and Protective Technologies,Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo 315201 |
|
|
|
|
Abstract With the development of the transportation, electric power, electronics and other fields,higher requirements have been put forward for copper alloys in strength and conductivity. The CuCrZr alloy is one of the ideal materials to meet these requirements. This paper summarizes the progress of the research on the alloying, designing and processing of CuCrZr alloy with the focus on the recent hot topics of CuCrZr alloys, discusses the influence of the processing methods presently under investigation on the microstructure and properties of CuCrZr alloy. The prospective research topics of the CuCrZr alloy have been also proposed.
|
|
Published: 10 February 2018
Online: 2018-02-10
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
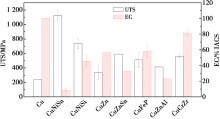
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and electrical conductivity (EC) of some copper alloys [1,2,3,4,5,6]
|

|
|
Relationship of the ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and the electrical conductivity (EC) of CuCrZr,CuCr,CuZr and some other commercially copper alloys[12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19]
|
|
|
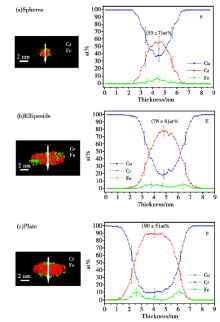
3D reconstruction of the precipitates in Cu-1Cr-0.1Zr alloy and the element profiles (the arrows indicate the location of the profiles; sampling thickness: 1 nm) [25]
|
|
|
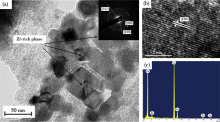
TEM image of sintered Cu-1Cr-0.65Zr alloy after aging at 450 ℃ for 4 h: (a) bright-field image and SAED pattern;(b) the HRTEM of the precipitate particles; (c) EDX of the precipitate particles[28]
|

Processing
methods | Alloys | Condition | σb/MPa | Conductivity
%IACS | Vacuum
induction
melting | Cu-(0.3—1)Cr-(0.03—0.2)Zr-X
(X=RE,Ti,Mg,etc.) | Solution-deformation-aging [13-14,24,32] | 425—590 | 75—83 | | Solution-aging[33,34] | 350—450 | 61—85 | | Secondary aging[35,36,37,38] | 480—1 120 | 67—90 | | Solution-SPD-aging[19,39-41] | 700—1 750 | 26—85 | Powder
metallurgy | Cu-(0.5—1.5)Cr-(0.05—0.5)Zr-Ti | Aging[42,43] | 400—450 | 78—85 | | Deformation-aging[44] | 600 | 62 | Non-vacuum
melting | Cu-(0.3—0.8)Cr-(0.15—0.45)Zr-X
(X=RE,Mg) | Solution-deformation-aging[45,46,47] | 450—540 | 78—85 | Rapid
solidification | Cu-0.3Cr-0.15Zr-0.05Mg | Aging[48] | 378 | 70 |
|
|
Properties of CuCrZr alloy prepared by different processes
|

| Defect | Resistance increment
μΩ·cm | | Vacancy (1%,atom fraction) | 1.6 | | Solution atom (1%,atom fraction) | 2.5 | | Grain boundary/(cm2/cm3) | 31.2×10-7 | | Dislocation/(cm/cm3) | 1.0×10-7 |
|
|
Effect of different crystal defects on the resistivity of Cu and Cu alloys[49,50]
|
|
|
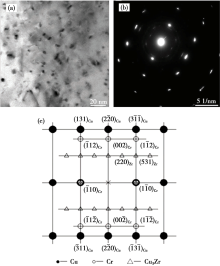
Bright field TEM micrographs and SAED patterns of 60% cold rolled Cu-0.81Cr-0.12Zr-0.05La-0.05Y specimens after aging at 773 K for 60 min[22]
|
|
|
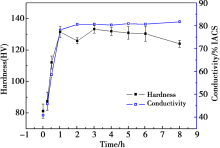
The microhardness and conductivity of Cu-0.8Cr-0.09Zr alloy aged at 450 ℃ for various time
|
|
|
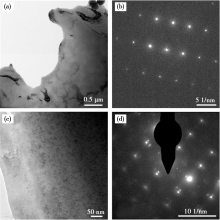
The Microstructure and SAED pattern of Cu-0.8Cr-0.09Zr alloy:(a,b)solution state;(c,d)solution-aging state
|
|
|
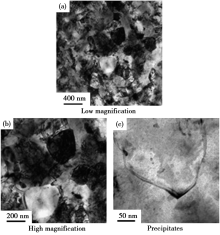
TEM micrographs of an 8th ECAPed Cu-0.8Cr-0.08Z sample after aging at 425 ℃ for 240 min[57]
|
|
|
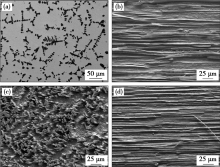
Microstructures of Cu-15Cr-0.24Zr composites with different deformation strains: (a) as-cast;(b) ε=2.41,longitudinal;(c) ε=2.41,transversal; (d) ε=6.44,longitudinal[62]
|
| 1 | Yin Zhimin, Zhang Shenglong . Hotspots and development trends of high strength and high conductivity copper alloy research[J]. Mi-ning and Metallurgical Engineering, 2002,22(2):1(in Chinese). | | 1 | 尹志民, 张生龙 . 高强高导铜合金研究热点及发展趋势[J]. 矿冶工程, 2002,22(2):1. | | 2 | Martienssen W, Warlimont H . Springer handbook of condensed mater and materials data[M]. Germany:Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2005: 296. | | 3 | Zhang Guojun, Su Juanhua . Finite element analysis of bending springback of copper alloy material for lead frame[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2011,40(7):91(in Chinese). | | 3 | 张国军, 苏娟华 . 引线框架用铜合金材料弯曲回弹有限元分析[J]. 热加工工艺, 2011,40(7):91. | | 4 | Dai J Y, Yin Z M, Song L P , et al. Microstructure and pro-perties evolution of Cu-2.5Fe-0.03P alloy under different treatment conditions[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009,19(11):1969(in Chinese). | | 4 | 戴姣燕, 尹志民, 宋练鹏 , 等. 不同处理状态下Cu-2.5Fe-0.03P合金的组织与性能演变[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2009,19(11):1969. | | 5 | Ghosh G, Miyake J, Fine M E . The systems-based design of high-strength, high-conductivity alloys[J]. JOM, 1997,49(3):56. | | 6 | Gholami M, Vesely J, Altenberger I , et al. Influence of grain size and precipitation hardening on high cycle fatigue performance of CuNiSi alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2017,684:524. | | 7 | 郭青蔚, 王桂生, 郭庚辰 . 常用有色金属二元合金相图集[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2010: 131. | | 8 | Zhou Zhiming, Wang Yaping, Xia Hua , et al. Research development of manufacture processing of Cu-Cr alloy[J]. Materials Review, 2008,22(3):44(in Chinese). | | 8 | 周志明, 王亚平, 夏华 , 等. CuCr合金制备技术的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2008,22(3):44. | | 9 | Su J, Dong Q, Liu P , et al. Research on aging precipitation in a Cu-Cr-Zr-Mg alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2005,392(1):422. | | 10 | Naotsugu I . Behavior of precipitation and recrystallization affect upon texture of CuCrZr alloy[J]. Journal of the Japan Copper and Brass Research Association, 1993,32:115. | | 11 | Pang Y, Xia C, Wang M , et al. Effects of Zr and (Ni, Si) additions on properties and microstructure of Cu-Cr alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014,582:786. | | 12 | Muramatsu N, Kimura H, Inoue A . Microstructures and mechanical properties of highly electrically conductive Cu-0.5, Cu-1 and Cu-2at%Zr alloy wires[J]. Materials Transactions, 2013,54(2):176. | | 13 | Muramatsu N, Goto T . Microstructures and mechanical and electrical properties of hypoeutectic Cu-1, Cu-3 and Cu-5at% Zr alloy wires preprocessed by spark plasma sintering[J]. Materials Transactions, 2013,54(7):1213. | | 14 | Islamgaliev R K, Nesterov K M, Bourgon J , et al. Nanostructured Cu-Cr alloy with high strength and electrical conductivity[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2014,115(19):194. | | 15 | Dobatkin S V, Gubicza J, Shangina D V , et al. High strength and good electrical conductivity in Cu-Cr alloys processed by severe plastic deformation[J]. Materials Letters, 2015,153:5. | | 16 | Liu Q, Zhang X, Ge Y , et al. Effect of processing and heat treatment on behavior of Cu-Cr-Zr alloys to railway contact wire[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2006,37(11):3233. | | 17 | Su J, Liu P, Li H , et al. Phase transformation in Cu-Cr-Zr-Mg alloy[J]. Materials Letters, 2007,61(27):4963. | | 18 | Hou Dongjian, Wu Lei, Gao Dawei , et al. Effect of magnesium silicon composite microalloying on high strength and high conductivity Cu-Cr-Zr alloy aging process[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2016,41(10):102(in Chinese). | | 18 | 侯东健, 武磊, 高大伟 , 等. 镁硅复合微合金化对高强高导铜铬锆合金时效过程的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2016,41(10):102. | | 19 | Pan Z, Chen J, Li J . Microstructure and properties of rare earth-containing Cu-Cr-Zr alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015,25(4):1206. | | 20 | Zhang Y, Huili S, Volinsky A A , et al. Hot deformation and dynamic recrystallization behavior of the Cu-Cr-Zr-Y alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2016,25(3):1150. | | 21 | Zhang Y, Sun H, Volinsky A A , et al. Dynamic recrystallization behavior and processing map of the Cu-Cr-Zr-Nd alloy[J]. Springer Plus, 2016,5(1):1. | | 22 | Saray O . Biaxial deformation behavior and formability of precipita-tion hardened ultra-fine grained (UFG) Cu-Cr-Zr alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2016,656:120. | | 23 | Verhoeven J D, Spitzig W A, Jones L L , et al. Development of deformation processed copper-refractory metal composite alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 1990,12(2):127. | | 24 | Hatakeyama M, Toyama T, Nagai Y , et al. Nanostructural evolution of Cr-rich precipitates in a Cu-Cr-Zr alloy during heat treatment studied by 3 dimensional atom probe[J]. Materials Transactions, 2008,49(3):518. | | 25 | Chbihi A, Sauvage X, Blavette D . Atomic scale investigation of Cr precipitation in copper[J]. Acta Materialia, 2012,60(11):4575. | | 26 | Sarin V K, Grant N J . Cu-Zr and Cu-Zr-Cr alloys produced from ra-pidly quenched powders[J]. Metallurgical Transactions, 1972,3(4):875. | | 27 | Batawi E, Morris D G, Morris M A . Effect of small alloying additions on behaviour of rapidly solidified Cu-Cr alloys[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1990,6(9):892. | | 28 | Zhou J, Zhu D, Tang L , et al. Microstructure and properties of powder metallurgy Cu-1% Cr-0.65% Zr alloy prepared by hot pres-sing[J]. Vacuum, 2016,131:156. | | 29 | Zhang Y, Volinsky A A, Tran H T , et al. Aging behavior and precipitates analysis of the Cu-Cr-Zr-Ce alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2016,650:248. | | 30 | Krishna S C, Rao G S, Jha A K , et al. Strengthening in high strength Cu-Cr-Zr-Ti alloy plates produced by hot rolling[J]. Mate-rials Science and Engineering:A, 2016,674:164. | | 31 | Chen X H, Hou B, Wang Z D . Formation of an abnormal lamellar precipitate in Cu-Cr-Zr-Mg-Ce nanocomposite during solution treatments[J]. Materials Research Innovations, 2015,19(sup5):1333. | | 32 | Li Si, Jiang Yexin, Li Zhou . Effect of thermomechanical treatment on Microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-2.7Ti-0.15Mg-0.1Ce-0.1Zr alloy[J]. Journal of Heat Treatment, 2016,37(3):127(in Chinese). | | 32 | 李思, 姜业欣, 李周 . 形变热处理对Cu-2.7Ti-0.15Mg-0.1Ce-0.1Zr合金组织和性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2016,37(3):127. | | 33 | Cheng J Y, Yu F X, Shen B . Solute clusters and chemistry in a Cu-Cr-Zr-Mg alloy during the early stage of aging[J]. Materials Letters, 2014,115:201. | | 34 | Cheng J Y, Shen B, Yu F X . Precipitation in a Cu-Cr-Zr-Mg alloy during aging[J]. Materials Characterization, 2013,81:68. | | 35 | Liu Y, Wang D J , Tian B H. Aging behavior of Cu-Cr-Zr-Y alloy[J].Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 311- 313:2005. | | 36 | Zhou Haitao, Zhong Jianwei, Zhou Xiao , et al. Effect of multi-step thermomechanical treatments on microstructure and properties of Cu-Cr-Zr alloy[J].Journal of Heat Treatment,2009(3):141(in Chinese). | | 36 | 周海涛, 钟建伟, 周啸 , 等. 多级形变时效对Cu-Cr-Zr合金组织和性能的影响[J].材料热处理学报,2009(3):141. | | 37 | Xie H F, Peng L J, Wang Z H , et al. Effects of two-stage solution heat treatments on microstructures and properties of Cu-Cr-Zr alloy[J].Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2013, 423- 426:230. | | 38 | Lin G B, Wang Z D, Zhang M K , et al. Heat treatment method for making high strength and conductivity Cu-Cr-Zr alloy[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2011,27(5):966. | | 39 | Shangina D V, Bochvar N R, Gorshenkov M V , et al. Influence of microalloying with zirconium on the structure and properties of Cu-Cr alloy after high pressure torsion[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2016,650:63. | | 40 | Shakhova I, Yanushkevich Z, Fedorova I , et al. Grain refinement in a Cu-Cr-Zr alloy during multidirectional forging[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2014,606:380. | | 41 | Sun L X, Tao N R, Lu K . A high strength and high electrical conductivity bulk CuCrZr alloy with nanotwins[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2015,99:73. | | 42 | Krishna S C, Rao G S, Jha A K , et al. Strengthening in high strength Cu-Cr-Zr-Ti alloy plates produced by hot rolling[J]. Mate-rials Science and Engineering:A, 2016,674:164. | | 43 | Ipek M. The effect of aging parameters on properties of PM Cu-Cr-Zr alloy [C]∥Metal 2014: 23rd International Conference on Metallurgy and Materials.Brno,Czech Republic, 2014. | | 44 | Qin Y Q, Wu Y C, Wang Y , et al. Preparation of Cu-Cr-Zr/AlN nanocomposites and their mechanical and conductive properties[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011,239:2756. | | 45 | Tao Yeqing, Liu Ping , et al. Study on the properties of nonvacuum melting Cu-Cr-Zr alloy[J].China Foundry,2010(10):1020(in Chinese). | | 45 | 陶业卿, 刘平 , 等. 非真空熔炼Cu-Cr-Zr合金的性能研究[J].铸造,2010(10):1020. | | 46 | Qin Y Q, Wu Y C, Wang Y, et al. Preparation of Cu-Cr-Zr/AlN nanocomposites and their mechanical and conductive properties[J].Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 239-242:2756. | | 47 | Kermajani M, Raygan S, Hanayi K , et al. Influence of thermomechanical treatment on microstructure and properties of electroslag remelted Cu-Cr-Zr alloy[J]. Materials & Design, 2013,51:688. | | 48 | Tenwick M J, Davies H A . Enhanced strength in high conductivity copper alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1988,98:543. | | 49 | Tavassoli A A F . Materials design data for fusion reactors[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1998,258:85. | | 50 | Huaqing L I , Shuisheng X I E, Pengyue W U, et al. Study on improvement of conductivity of Cu-Cr-Zr alloys[J]. Rare Metals, 2007,26(2):124. | | 51 | Zhu Chengcheng, Ma Aibin , et al. Research status and development trend of high strength and high conductivity copper alloy[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2013,42(2):15(in Chinese). | | 51 | 朱承程, 马爱斌 , 等. 高强高导铜合金的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 热加工工艺, 2013,42(2):15. | | 52 | Zhang X P, Yang B, Li M M , et al. Anti-burning loss of Cu-Cr-Zr alloys melted under non-vacuum conditions[J].Nonferrous Metals Science & Engineering,2015(3):36(in Chinese). | | 52 | 张小平, 杨斌, 李明茂 , 等. 非真空熔铸CuCrZr合金的抗烧损研究[J].有色金属科学与工程,2015(3):36. | | 53 | Ding Zongye, Jia Shuguo, Guo Wangwan , et al. Thermal deformation behavior and critical conditions of dynamic recrystallization of Cu-Cr-Zr alloy in non-vacuum casting[J].Rare Metal Materials and Engineering,2014(2):408(in Chinese). | | 53 | 丁宗业, 贾淑果, 郭望望 , 等. 非真空熔铸Cu-Cr-Zr合金的热变形行为及动态再结晶临界条件[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2014(2):408. | | 54 | Su Juanhua, Li Hejun , et al. Effects of solution aging and rapid solidification aging on aging properties of Cu-Cr-Zr-Mg alloy[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2004,35(4):439(in Chinese). | | 54 | 苏娟华, 李贺军 , 等. 固溶时效和快速凝固时效对Cu-Cr-Zr-Mg合金时效性能的影响[J]. 功能材料, 2004,35(4):439. | | 55 | Wang K, Liu K F, Zhang J B . Microstructure and properties of aging Cu-Cr-Zr alloy[J]. Rare Metals, 2014,33(2):134. | | 56 | Mishnev R, Shakhova I, Belyakov A , et al. Deformation microstructures, strengthening mechanisms, and electrical conductivity in a Cu-Cr-Zr alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2015,629:29. | | 57 | Purcek G, Yanar H, Demirtas M , et al. Optimization of strength, ductility and electrical conductivity of Cu-Cr-Zr alloy by combining multi-route ECAP and aging[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:A, 2016,649:114. | | 58 | Abib K, Azzeddine H, Tirsatine K , et al. Thermal stability of Cu-Cr-Zr alloy processed by equal-channel angular pressing[J]. Mate-rials Characterization, 2016,118:527. | | 59 | Zhilyaev A P, Shakhova I, Morozova A , et al. Grain refinement kinetics and strengthening mechanisms in Cu-0.3Cr-0.5Zr alloy subjected to intense plastic deformation[J]. Materials Science and Enginee-ring A, 2016,654:131. | | 60 | Abib K , Balanos J A M, Alili B, et al. On the microstructure and texture of Cu-Cr-Zr alloy after severe plastic deformation by ECAP[J]. Materials Characterization, 2016,112:252. | | 61 | Bi L , et al. Effect of Zr addition on Cr fibres and properties of Cu-15Cr in-situ composites[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2012,33:14. | | 62 | Jia Shuguo, Liu Ping, Song Kexing , et al. Microstructure and pro-perties of Cu-Cr-Zr in situ composite[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2010,20(7):1334(in Chinese). | | 62 | 贾淑果, 刘平, 宋克兴 , 等. Cu-Cr-Zr原位复合材料的组织与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2010,20(7):1334. | | 63 | Uddin S M, Mahmud T, Wolf C , et al. Effect of size and shape of metal particles to improve hardness and electrical properties of carbon nanotube reinforced copper and copper alloy composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2010,70(16):2253. | | 64 | Cheng Jianyi, Wang Mingpu, Zhong Weijia , et al. The microstructure and properties of the internal oxidation of Cu-Al2O3 alloy[J]. Journal of Heat Treatment, 2003,24(1):23(in Chinese). | | 64 | 程建奕, 汪明朴, 钟卫佳 , 等. 内氧化法制备的Cu-Al2O3合金的显微组织与性能[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2003,24(1):23. | | 65 | Ichikawa K, Achikita M . Electric conductivity and mechanical pro-perties of carbide dispersion-strengthened copper prepared by compocasting[J]. Materials Transactions,JIM, 1993,34(8):718. | | 66 | Sheikh M, Mahmud T, Wolf C , et al. Effect of size and shape of metal particles to improve hardness and electrical properties of carbon nanotube reinforced copper and copper alloy composites[J]. Compo-sites Science and Technology, 2010,70(16):2253. | | 67 | Zhang S, Li R, Kang H , et al. A high strength and high electrical conductivity Cu-Cr-Zr alloy fabricated by cryorolling and interme-diate aging treatment[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2017,680:108. | | 68 | Wang W, Li R, Zou C , et al. Effect of direct current pulses on mechanical and electrical properties of aged Cu-Cr-Zr alloys[J]. Materials & Design, 2016,92:135. | | 69 | Li Rengeng, Zhang Shaojian, Kang Huijun , et al. Microstructure and texture evolution in the cryorolled CuZr alloy[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017,693:592. |
|
|
|
|

 渝公网安备50019002502923号 © Editorial Office of Materials Reports.
渝公网安备50019002502923号 © Editorial Office of Materials Reports.
 2018, Vol. 32
2018, Vol. 32 